How To Restore Multiple SQL Databases At One TimeWednesday, September 9, 2015 - by Keith A. SmithOne of the things I had on my to-do list was to take backups of a few SQL databases used by production systems, this way testing could be done in a separate environment. During the last Maintenance window, I got a chance to do this. The steps were: 1. Spin up a new server (perform normal S.O.P for provisioning) 2. Install SQL Server 3. On the new test SQL server, Add/create security logins (they need to match the source, which would the SQL server where the database came from) 4. On prod servers, that had multiple databases I setup a Maintenance plan that would take a full backup of the databases I selected. 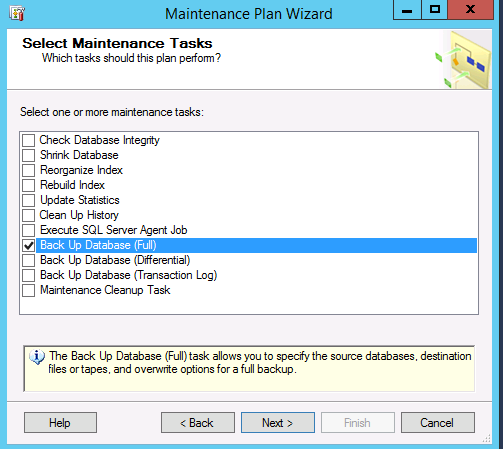 I did this because it was a quick and easy way to backup multiple databases in one fell swoop. I stop the services on the application servers to halt data being written then execute the Maintenance plan. At this point, I move all the backups to the new test SQL server. I now have backups of all the databases I wanted in. bak files. I now am tasked with having to restore quite a few databases to this new SQL server. It would be great if I could do the reverse of #4 and restore multiple SQL databases at the same time, unfortunately that is not an option from within the SQL Management studio. I could have created SSIS Packages to copy the data between data sources but chose not to on this opportunity. I had an idea! If you go in the SQL Management Studio, then go through all the steps to do the SQL database restore, choose a source and destination database. Then go to the script drop down to copy the T-SQL script  which looked like this RESTORE DATABASE [DBNAME] FILE = N'DBNAME' FROM DISK = N'v:\DBNAME_backup_2015_09_09_RANDOM.bak' WITH FILE = 1, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10 GO Where the DBNAME is that would be the database name as it would show in the SQL Management studio. Now with the T-SQL script there I wanted to get the names of all the SQL backups, for this I ran the following from a command line driveletter:\folder\dir /b>list.txt This will create the text file inside that folder. If you want the file output elsewhere, use a fully qualified name. Remember that Windows uses \ as the directory delimiter, not / Now using the list.txt file I created, I take the names of the databases and insert them in the T-SQL script where it says DBNAME. I do this for each database using some other methods to speed this part up. Once this is completed I execute the query; it took a few minutes, but results show no errors when completed. I refresh the Object Explorer, and now all the databases are attached. I was able to change a string on a test application server, and point it at the new test SQL to confirm that the application was going to work. A Restart of a few services and success! Data is present and current at least at the time of the backup.
|
| Tweet |


 Comments
Comments
